When it comes to video content, resolution is key to a great viewing experience. With technology evolving rapidly, we now have multiple video resolution options. Two common choices are SD (Standard Definition) and HD (High Definition). Many people want to understand the differences between SD and HD to make informed decisions.
In this blog, we will dive into the distinctions between HD and SD video resolutions and how they affect your overall viewing pleasure.
Contents
SD vs. HD: What is Standard Definition (SD)?
Standard Definition (SD) has been a cornerstone in the history of video and television, known for its widespread compatibility and cost-effectiveness. However, in the era of HD (High Definition) and UHD (Ultra High Definition) content, the limitations of SD—such as its lower visual quality and decreasing availability—are becoming more noticeable.
As technology evolves, SD is being gradually replaced by higher-resolution formats. In this section, we’ll delve into what SD is and how it compares to HD.
What is SD?
Standard Definition (SD) refers to a specific video resolution format commonly used in television and digital media. It is characterized by a lower pixel count and aspect ratio compared to HD and UHD. Typically, SD resolutions are 720×480 pixels for NTSC systems and 720×576 pixels for PAL systems. SD content is often viewed on older television sets and devices that do not support higher resolutions.
Pros of SD
- Compatibility: One major advantage of SD is its broad compatibility with various devices. Older TVs, DVD players, and other legacy hardware can easily display SD content, making it accessible to a wider audience, especially in areas where HD or UHD technology isn’t prevalent.
- Lower Bandwidth Requirements: SD requires significantly less bandwidth for streaming or downloading compared to HD or UHD. This makes it ideal for regions with limited internet connectivity or slower speeds, allowing users to enjoy videos without buffering or lag.
- Cost-Effective: Producing and distributing SD content is generally more affordable than HD or UHD. The lower resolution reduces the need for advanced equipment, sophisticated software, and extensive storage. This cost-efficiency benefits content creators, broadcasters, and consumers alike.
Cons of SD
- Lower Visual Quality: The most significant drawback of SD is its inferior visual quality compared to HD and UHD. With fewer pixels and a smaller aspect ratio, SD content lacks the sharpness, detail, and color accuracy that viewers have come to expect from modern high-resolution media.
- Limited Viewing Experience: SD’s lower resolution can limit the immersive experience of watching movies, TV shows, and other multimedia content. The lack of detail and clarity can lessen viewer engagement and enjoyment, making the experience feel less cinematic and lifelike.
- Decreasing Availability: As HD and UHD become standard, SD is gradually becoming obsolete. Many broadcasters and streaming platforms are focusing on higher-resolution formats, which means new SD content is becoming increasingly rare. This shift limits options for those who still rely on SD-compatible devices.
In summary, while SD has its advantages, the move towards HD and UHD is making SD a less viable option for high-quality viewing experiences.
HD vs. SD: Understanding High Definition (HD)
High Definition (HD) technology has revolutionized the way we experience visual content, making it more immersive and lifelike. With enhanced detail, vibrant colors, and a wider aspect ratio, HD content elevates the viewer’s experience. However, it’s important to weigh potential drawbacks, such as higher bandwidth needs, increased costs, compatibility issues, and larger file sizes.
In this section, we’ll explore the key differences between SD and HD resolution:
What is HD?
High Definition (HD) refers to video and image quality that offers greater detail, clarity, and resolution than Standard Definition (SD). HD content has a minimum resolution of 720 pixels in height and 1280 pixels in width. The higher the resolution, the sharper and more detailed the image or video appears.
Pros of HD
- Enhanced Visual Experience: HD content delivers a more immersive and realistic viewing experience. The increased resolution and clarity make images and videos appear sharper, bringing out intricate details that are often missed in lower-quality formats.
- Vibrant Colors and Contrast: HD technology incorporates advanced color reproduction and contrast enhancement techniques, resulting in more vibrant colors. This added depth and realism make the content more engaging and enjoyable.
- Wide Compatibility: HD content is widely supported across various devices and platforms, including TVs, computers, smartphones, and streaming services. This broad compatibility allows users to enjoy HD content seamlessly on their preferred devices.
Cons of HD
- Higher Bandwidth and Storage Requirements: Due to its higher resolution, HD content demands more bandwidth and storage space. Streaming or downloading HD videos may use more data, which can be a concern for those with limited internet plans or low-capacity devices.
- Increased Costs: HD technology generally costs more than SD. HD-capable TVs, cameras, and other devices tend to have higher price tags. Additionally, subscribing to HD streaming services may require a higher subscription fee.
- Compatibility Limitations: While HD content is widely supported, older devices or systems may not be compatible with HD formats. This limitation can prevent users from fully enjoying the benefits of HD if they lack compatible equipment.
In summary, HD offers a superior viewing experience with enhanced visual quality and immersive details. However, it’s essential to consider factors like bandwidth, cost, and compatibility when transitioning from SD to HD.
SD vs. HD: What are the Differences?
HD vs. SD Streaming (YouTube, Netflix)
When it comes to streaming platforms like Netflix and YouTube, users can choose between various resolutions, including SD (Standard Definition) and HD (High Definition). The choice often depends on the available internet connection and device capabilities.
- Visual Quality: Compared to HD, SD might offer blurry visuals, which can be unsatisfactory for viewers seeking clear picture quality. HD provides sharper and more detailed images, enhancing the overall viewing experience.
- Internet Connection: SD content can be beneficial for slow or unstable internet connections, as it requires less bandwidth. However, the trade-off is lower visual quality. HD requires a more stable and higher-speed connection to avoid buffering issues and to deliver a clear image.
HD vs. SD Device Compatibility
Device compatibility differs significantly between SD and HD videos. Here’s how each format performs on various devices:
- Modern Devices: Laptops, smartphones, tablets, and newer TVs primarily support HD resolution. These devices are designed to handle the higher resolution and provide a more immersive and visually appealing experience.
- Older Devices: Older equipment, such as DVD players and older televisions, are more suited for SD content. These devices may not support HD formats, making SD a more practical choice for viewing.
HD vs. SD Video Resolution Quality
Here’s a quick comparison of SD and HD video resolutions:
SD vs. HD: When to Use Them?
When to Use SD Resolution?
- Older Devices: SD resolution is well-suited for older devices with lower display resolutions and limited processing power. These devices might struggle with HD content, but can handle SD efficiently.
- Slow Internet Connection: If you have a slow internet connection or a limited data plan, streaming videos in SD can help minimize buffering and reduce data usage. SD videos require less bandwidth, making them more practical for low-bandwidth situations.
- Smaller File Sizes: SD videos have significantly smaller file sizes compared to HD videos, making them ideal for quick downloads and limited storage capacities.
When to Use HD Resolution?
- Modern Screens: HD resolution is perfect for larger screens, such as modern televisions, computer monitors, and tablets. These devices can display HD content to its full potential, offering a more immersive experience.
- Visual Quality: HD resolution provides increased clarity and detail, enhancing the enjoyment of content that relies heavily on high-quality visuals. This includes movies, documentaries, and high-definition video productions.
- Enhanced Viewing Experience: Overall, HD content delivers a more visually appealing and engaging viewing experience, making it the preferred choice when visual quality is a priority.
In summary, use SD resolution for older devices, slower internet connections, and situations where smaller file sizes are essential. Opt for HD resolution when you want to fully appreciate the visual quality on modern screens and enjoy a more immersive viewing experience.
What to Consider When Upgrading from SD to HD?
Upgrading from SD (Standard Definition) to HD (High Definition) can significantly enhance your viewing experience. However, there are important factors to consider before making the switch:
- Content Availability: Verify if the HD version of the content you wish to upgrade is available. Some platforms may offer an upgrade option for SD purchases to HD, while others may not. Check your chosen platform’s policies and catalog to ensure availability.
- Device Compatibility: Ensure your devices such as TVs, monitors, or streaming devices support HD playback. HD content demands compatible hardware to display the enhanced resolution and quality. Check your device specifications to confirm compatibility before upgrading.
- Internet Connection: HD content typically requires a faster and more stable internet connection compared to SD. Make sure your internet connection can handle the higher bandwidth demands for streaming or downloading HD content without interruptions.
- Storage Space: HD files are generally larger than SD files. Assess your storage space to ensure you have enough capacity for the increased file sizes that come with HD content. You might need to upgrade your storage options if required.
Considering these factors will help you make an informed decision when upgrading from SD to HD, ensuring a smooth transition and an improved viewing experience.
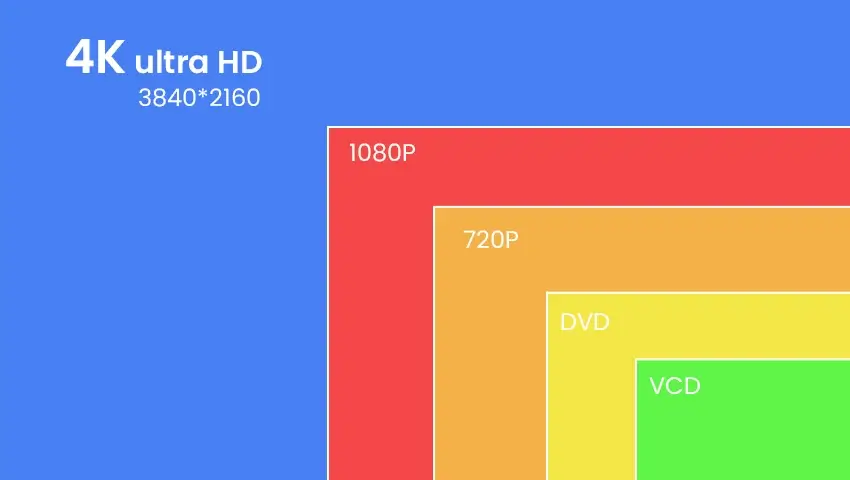
Upgrade to Higher Resolution – 4K
Upgrading to a 4K resolution means capturing images with 8 million pixels—specifically, arranged like 3840×2160 pixels. This higher megapixel count translates to more detail, enabling you to print larger photos without losing quality or clarity.
4K POE Surveillance Cameras Security Monitor Systems
- Smart Person/Vehicle Detection
- Customize Detection Zone
- 4K Starlight Night Vision
- 24/7 Video & Audio Recording
- Access Remotely & Flexibly
- Two Way Audio
FAQs
1. Is HD or SD Better?
HD is generally superior to SD in terms of video quality. With resolutions like 1080p or 720p, HD provides sharper and more detailed images compared to SD’s 480p resolution. However, factors like display size and viewing distance can influence the perceived difference in quality.
2. Is There a Big Difference Between SD and HD on Amazon?
The difference between SD and HD on Amazon depends on the content being streamed. Some content is available in both SD and HD formats, while others may only come in one format. Generally, HD offers significantly sharper and more detailed images than SD.
3. Can You Tell the Difference Between SD and HD?
Yes, especially on larger screens or when comparing side by side. HD offers higher resolution and better image quality, resulting in sharper details and more vibrant colors. The perceived difference may vary based on viewing distance and the quality of the source material.
Conclusion
The key differences between SD and HD video resolution lie in clarity, detail, and overall viewing experience. While SD is suitable for older devices and slower internet connections, it lacks the crispness and sharpness of HD. HD resolution significantly enhances image quality, making it the preferred choice for most viewers.