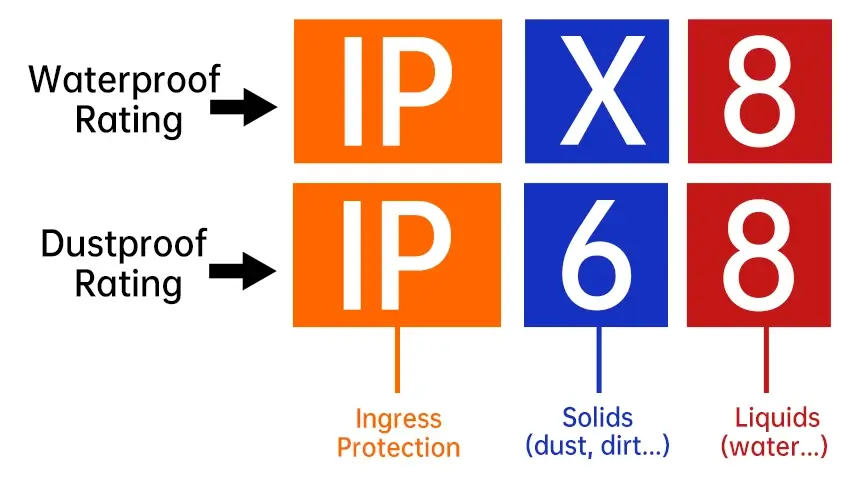
Whether you’re selecting a security camera for outdoor use, a rugged smartphone for adventurous pursuits, or industrial equipment designed to withstand harsh environments, the IP66 vs IP67 rating is a critical factor. This article provides a practical comparison of these two common Ingress Protection standards, empowering you to choose the right level of defense against dust and water. The IP (Ingress Protection) rating system is a crucial tool for determining the level of protection electronic devices have against dust and water. As technology continues to evolve and devices are increasingly used in diverse environments, understanding the nuances between different IP ratings becomes essential. IP66 and IP67 are two commonly encountered ratings, each offering distinct levels of protection. This blog will explore the specifics of each rating, compare their features, and provide answers to common questions to help you make informed decisions about the protection level needed for your devices.
Contents
What are the features of IP66 vs IP67:
1. IP66:
Dust Protection: IP66 offers complete protection against dust ingress. It ensures that no dust can enter the device, providing a high level of dust resistance. This is particularly important for devices that are used in environments where dust is prevalent, such as industrial settings or outdoor locations with high levels of airborne particles.
Water Protection: The second digit, ‘6’, indicates that the device can withstand powerful water jets from any direction. This makes IP66 suitable for environments where water spray is a concern, such as outdoor installations or industrial settings where water is used for cleaning. The protection against water jets ensures that the device remains functional even when exposed to highpressure water.
2. IP67:
Dust Protection: Like IP66, IP67 also provides complete protection against dust. It ensures that no dust can penetrate the device, maintaining its internal integrity. This level of protection is essential for devices that are exposed to dusty environments or need to maintain their functionality in the presence of airborne particles.
Water Protection: The ‘7’ in IP67 signifies that the device can be temporarily submerged in water up to 1 meter deep for up to 30 minutes without damage. This makes IP67 ideal for applications where there is a risk of accidental immersion or temporary submersion. It is suitable for devices that may be exposed to water splashes or need to operate in environments where water ingress is a concern.
IP66 vs IP67 function comparison:
1. Dust Protection:
Both IP66 and IP67 offer the same level of dust protection, ensuring complete resistance to dust ingress. This means that devices with either rating can be used in environments with high levels of dust without the risk of damage or malfunction.
2. Water Protection:
The primary difference between IP66 and IP67 lies in their water protection capabilities. IP66 is designed to handle powerful water jets, making it suitable for applications where water spray is the main concern. In contrast, IP67 is designed for temporary submersion, providing protection against water ingress even when the device is submerged. This makes IP67 a more suitable choice for devices that may be exposed to water immersion.
3. Use Cases:
IP66 is ideal for outdoor environments where water spray is common, such as in street lighting, outdoor surveillance cameras, and industrial equipment that is frequently cleaned with water. IP67 is more suitable for applications where there is a risk of immersion, such as underwater cameras, marine electronics, and devices used in environments with a risk of accidental immersion.
FAQs:
1. Which rating is better for outdoor use?
For general outdoor use where water spray is the primary concern, IP66 is sufficient. It provides excellent protection against water jets, ensuring that the device remains functional in outdoor environments. However, if there is a risk of immersion, such as in areas prone to flooding or where the device may be submerged in water, IP67 would be more appropriate.
2. Can IP66 devices be submerged in water?
No, IP66 devices are not designed for submersion. They can handle water jets but should not be submerged in water. Submerging an IP66 device in water can lead to water ingress and potential damage to the device.
3. Is IP67 suitable for longterm immersion?
IP67 is not designed for longterm immersion. It provides protection for temporary submersion up to 1 meter deep for 30 minutes. For applications that require longterm immersion, a higher IP rating, such as IP68, would be more suitable.
4. What are the common applications for each rating?
IP66 is commonly used in outdoor lighting, industrial equipment, and outdoor electronic displays. It is ideal for devices that are exposed to water spray but do not require protection against immersion. IP67 is often found in underwater cameras, marine electronics, and devices used in environments with a risk of accidental immersion. It is suitable for devices that need to withstand temporary submersion without damage.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, selecting the appropriate IP rating – IP66 or IP67 – is crucial for ensuring your device’s longevity and reliability, and hinges on the specific environmental risks it will encounter. If your primary concern is protection against powerful water jets, IP66 offers a suitable and cost-effective solution, making it ideal for environments where water spray is common. However, for scenarios where temporary submersion is a possibility, IP67 provides the necessary safeguard, guaranteeing functionality even after brief immersion. Understanding these distinctions empowers you to make informed decisions, safeguarding your investments and ensuring consistent performance, whether for outdoor lighting, industrial machinery, or marine electronics.