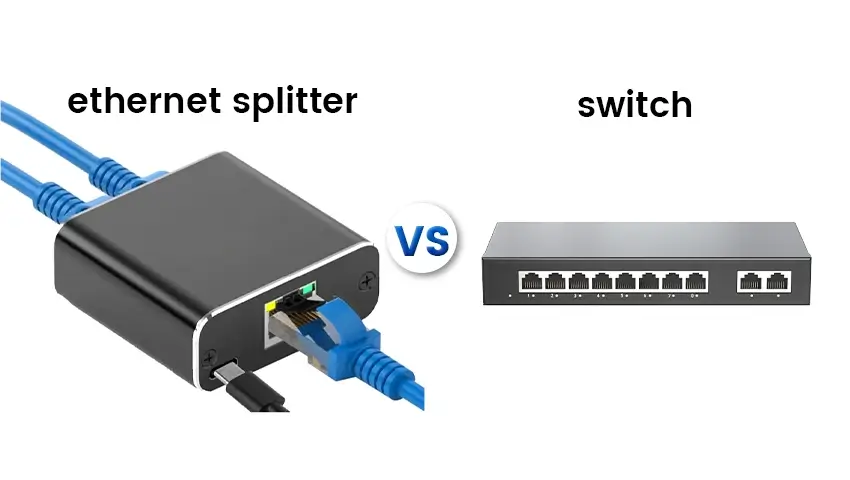
In the digital age, Ethernet connections are the backbone of our online lives. But when it comes to expanding your network, do you opt for an Ethernet splitter or a switch? Let’s dive into the world of networking and find out!
Contents
Basics of Ethernet Splitter and Switch
Ethernet splitters and switches are both used to connect multiple devices to a network but serve different purposes and are suitable for various scenarios.
1. Ethernet Splitter
An Ethernet splitter is a simple device that allows you to clone an Ethernet signal, connecting multiple devices to a single port. It’s like having a magic mirror that duplicates your connection!
How It Works:
Ethernet splitters enable two network connections to share a single Ethernet cable. They don’t increase the number of available network ports but allow you to connect two devices through a single cable. This setup can be useful for connecting devices over limited wiring but doesn’t manage network traffic.
Pros:
- Cost-Effective: It’s cheaper than a switch.
- Simple: No need for complex configurations.
Cons:
- Bandwidth Sharing: All devices share the same bandwidth, so if one device is downloading heavily, others may suffer.
- No Advanced Features: It’s a one-trick pony with no room for growth or security features.
Applications of Ethernet Splitters:
- Security Cameras: Ideal for connecting multiple cameras with limited cabling.
- Wireless Bridges: Used to connect two network segments with a single cable.
2. Network Switch
A network switch, on the other hand, is like a traffic cop for your network. It manages data flow, ensuring each device gets the bandwidth it needs without traffic jams.
How It Works:
A switch provides dedicated bandwidth to each device, significantly improving network performance and reliability. It uses MAC addresses to route data specifically to the intended device, reducing congestion and enabling efficient, high-speed connections between devices.
Pros:
- Performance: Each device gets its own lane on the information superhighway.
- Security: Advanced switches offer features like VLANs and access control.
- Scalability: Easy to add more devices as your network grows.
Cons:
- Cost: It’s more expensive than a splitter.
- Setup: Requires more technical know-how.
Applications of Ethernet Switches:
- Security Systems: Used for connecting multiple security devices such as cameras.
- VoIP Phones: To connect multiple phones in an office environment.
- Wireless Access Points (WAPs): Connect multiple WAPs in large spaces to ensure strong network coverage.
Ethernet Splitter vs. Hub vs. Switch
When comparing an Ethernet switch, hub, and splitter, it’s essential to understand their distinct functionalities:
- Hub: Broadcasts incoming data packets to all connected devices without filtering, potentially leading to network congestion.
- Splitter: Divides a single Ethernet connection into two, sharing bandwidth between devices without managing traffic.
- Switch: Intelligently routes data to intended devices and offers dedicated bandwidth, ideal for larger networks.
Ethernet Splitter vs. Router
A router, unlike a splitter, is a more advanced device designed to route data packets between different networks. It connects your local network to the internet, assigns local IP addresses, and may offer Wi-Fi. A splitter, in contrast, extends a single Ethernet connection to multiple devices but cannot manage or route traffic between networks.
Choosing Between Them
Splitter: Suitable for simple, small-scale networks or when connecting just a few devices. Ideal for home users with limited budget and minimal network demands.
Switch: Essential for businesses or complex networks where bandwidth, security, and scalability are priorities. It’s worth the investment for more reliable and faster connections.
Real-world Scenarios:
- Home User: A splitter may be sufficient for a few devices that don’t require much bandwidth.
- Small Business: A switch is better suited to handle additional devices and provides basic security.
- Enterprise: High-end switches are essential for extensive networks, supporting security, speed, and flexibility.
FAQs
1. What is the difference between an Ethernet splitter and an Ethernet switch?
An Ethernet splitter is a basic device that divides a single Ethernet connection into two, sharing the bandwidth without managing traffic. In contrast, an Ethernet switch connects multiple devices, providing each with dedicated bandwidth and intelligent traffic management, making it more suitable for complex networks.
2. Can an Ethernet switch function as a splitter?
No, an Ethernet switch cannot function as a splitter. Although it connects multiple devices to a network like a splitter, it goes further by managing data traffic and providing each device with dedicated bandwidth.
3. Do Ethernet splitters slow down the connection?
Ethernet splitters do not inherently slow down the connection, but since they share the bandwidth of a single cable between two devices, heavy use by both devices may impact performance. For high-speed or simultaneous use, a switch is recommended.
4. When should I use an Ethernet splitter over a switch?
A splitter is useful in simple setups where only two devices need to share one Ethernet line and traffic management isn’t a priority. For example, it’s often used to connect two devices in a home network or to extend a connection without extra cables.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between an Ethernet splitter and a switch is crucial for setting up a network that meets your needs. For a small setup, a splitter can save you money and offer simple connectivity. For larger networks or future growth, a switch provides better performance and more features. Choose wisely based on your specific needs!