Understanding the key differences between Bluetooth and 2.4GHz Wi-Fi is crucial for selecting the optimal wireless technology for various applications. In the ever-evolving landscape of wireless technology, these two frequencies stand out as workhorses of connectivity. Both are ubiquitous, facilitating the seamless interaction between our devices and enhancing our digital lives. But how do they stack up against each other, and which is the right choice for your specific needs? This blog post will dissect the nuances of Bluetooth and 2.4GHz Wi-Fi, examining their features, performance, and use cases, and addressing common queries to guide you through the decision-making process.
Contents
What are the features of Bluetooth vs 2.4GHz
Bluetooth technology has become an essential part of our daily lives, from wireless headphones to smart home devices. Here are some of its key features:
- Low Energy Consumption: Bluetooth is designed to consume minimal power, making it ideal for battery-operated devices that need to last for extended periods.
- Short Range: It typically operates within a range of 10 meters, which is suitable for personal area networks (PANs) but not for covering larger spaces.
- Versatility: Bluetooth is incredibly versatile, with the ability to connect a wide array of devices, from smartphones to wearables.
- Adaptability: It supports various profiles, such as A2DP for audio streaming and HID for keyboard and mouse connections.
- Version Updates: Bluetooth has seen several updates, with newer versions like Bluetooth 5.0 offering increased speed and range, as well as better coexistence with other wireless technologies.
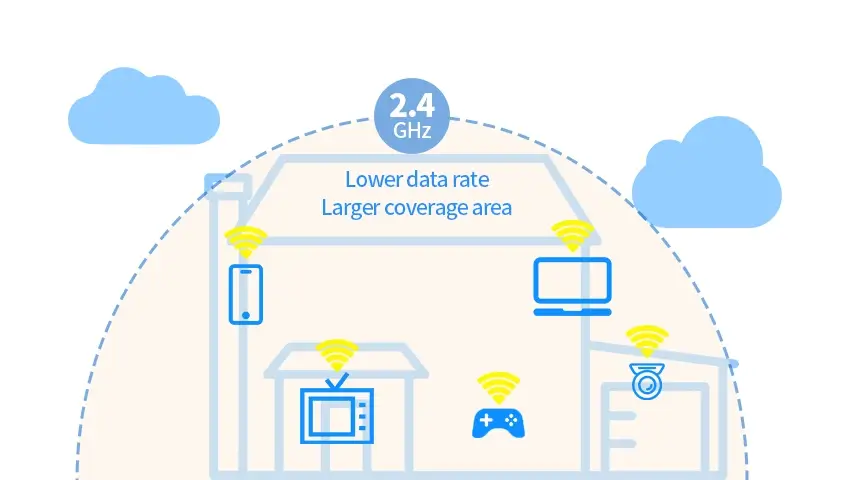
2.4GHz Wi-Fi is a staple in home and office networks, known for its reliability and speed. Here’s what sets it apart:
- Longer Range: 2.4GHz Wi-Fi can cover larger areas, making it suitable for home networks and larger office spaces.
- Higher Data Rate: It supports faster data transfer rates compared to standard Bluetooth, which is beneficial for streaming high-definition video and transferring large files.
- Interference: Operating on the 2.4GHz frequency, it is more prone to interference from other wireless devices, microwaves, and even some household appliances.
- Multiple Devices: 2.4GHz Wi-Fi networks can handle multiple connections simultaneously, which is crucial for environments with many connected devices.
- Standards: It follows Wi-Fi standards such as 802.11b/g/n, which operate on the 2.4GHz band, providing a stable and widely supported wireless connection.
Bluetooth vs 2.4GHz function comparison
When comparing Bluetooth and 2.4GHz Wi-Fi, it’s essential to consider their performance in various aspects:
Here is a comparison table of cat 6 and cat 6a:
FAQs
To further clarify the differences and help you make an informed decision, let’s address some common questions:
1. Which is better for gaming?
2.4GHz Wi-Fi is generally better for gaming due to its faster data rates and lower latency, which are crucial for a smooth gaming experience. However, some modern Bluetooth versions offer low latency modes, making them suitable for gaming as well, especially for wireless headphones.
2. Can Bluetooth and 2.4GHz Wi-Fi coexist without interference?
They can coexist, but due to operating on the same frequency band, there can be interference. Modern devices often have mechanisms to minimize this, such as frequency hopping in Bluetooth and channel bonding in Wi-Fi, which can allocate more bandwidth and reduce interference.
3. Is Bluetooth more secure than 2.4GHz Wi-Fi?
Both have security protocols in place. Wi-Fi networks can be more vulnerable to hacking if not properly secured, while Bluetooth has personal area network characteristics that can offer some level of security by default. However, both can be secured with proper configurations and updates.
Conclusion
The choice between Bluetooth and 2.4GHz Wi-Fi is not a one-size-fits-all answer. Bluetooth excels in low-power applications and short-range personal area networks, while 2.4GHz Wi-Fi is better for covering larger areas and handling high-speed data transfers. Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each will help you choose the right technology for your wireless connectivity needs. As technology continues to evolve, both Bluetooth and Wi-Fi are likely to improve, offering even more options for seamless connectivity in the future. Whether you’re a tech enthusiast, a home user, or a business professional, knowing the ins and outs of these wireless technologies will empower you to make the best choices for your devices and networks.